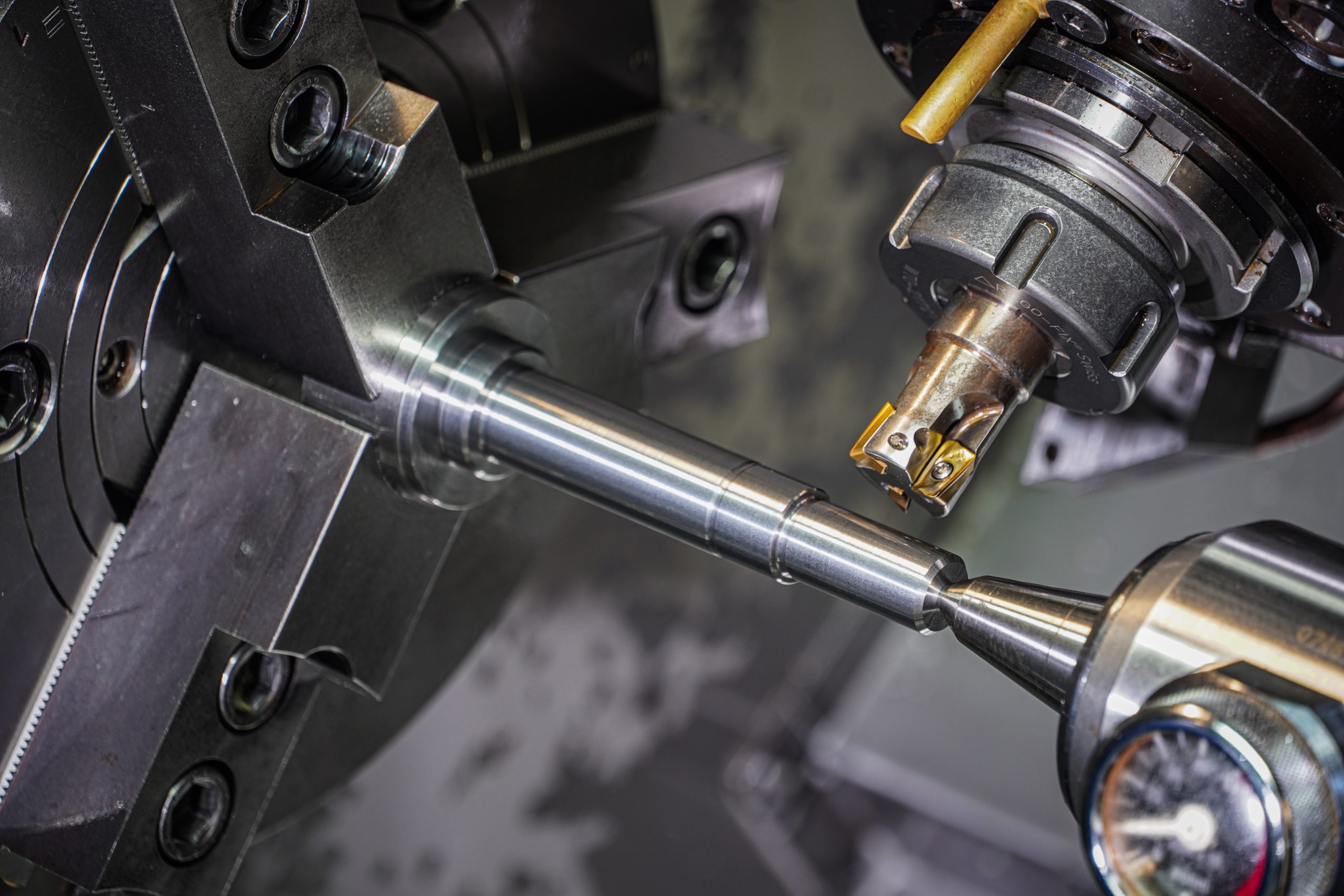
What is CNC Milling?
In the realm of modern manufacturing and prototyping, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling has revolutionized the way intricate and precise components are created. This advanced machining process utilizes computerized controls to guide the movement of cutting tools, resulting in high-quality outputs with utmost accuracy. In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of CNC milling, exploring its principles, benefits, applications, and its vital role in shaping numerous industries.
CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing technique that involves the removal of material from a workpiece using rotary cutters. The process is guided by pre-programmed computer instructions, which control the movement of the milling machine and its tools. These instructions specify the precise coordinates, speed, and depth of the cuts, ensuring consistent and repeatable results.
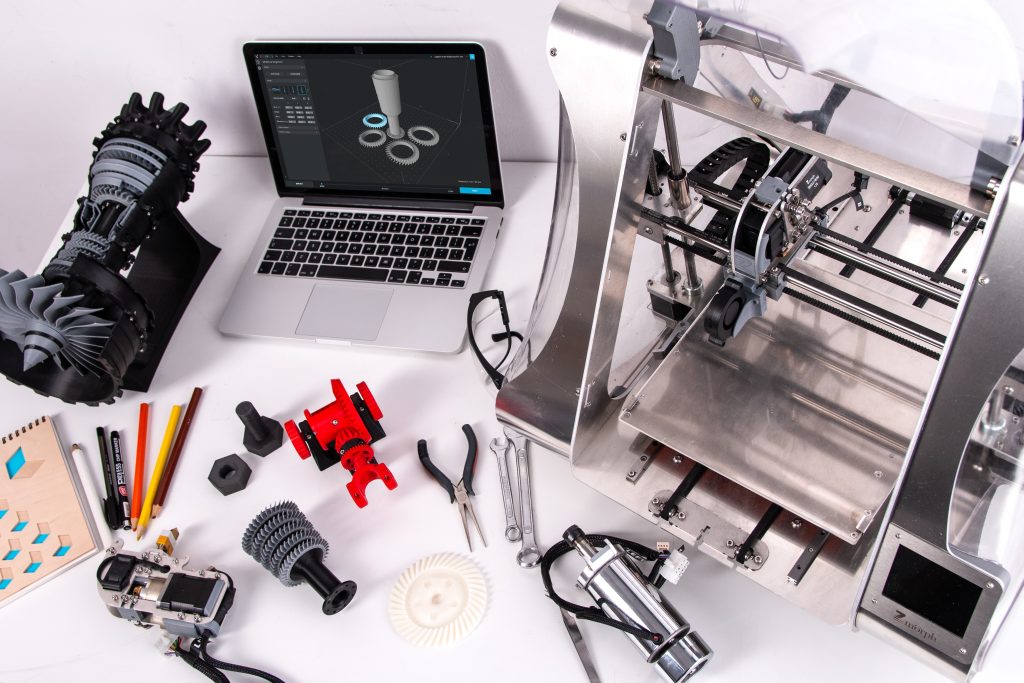

The CNC Milling Process:
- Design: The process begins with the creation of a digital design using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. The design specifies the dimensions, shapes, and features of the desired part.
- CAM Programming: The CAD file is then imported into Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software, where tool paths are generated. The CAM program determines the optimal cutting paths, taking into account factors such as tool selection, cutting speed, and material properties.
- Machine Setup: The workpiece is securely clamped to the milling machine’s bed or vice, and the appropriate cutting tools, such as end mills or drills, are selected. The tools are inserted into the machine’s tool holder, ready for operation.
- CNC Operation: The CAM program is transferred to the CNC milling machine’s control unit. The machine interprets the instructions and executes precise movements along the X, Y, and Z axes, controlling the tool’s position and depth of cut. The cutting tool removes material from the workpiece in accordance with the programmed tool paths.
- Finishing and Inspection: Once the milling process is complete, the part undergoes finishing operations, such as deburring or surface treatments, to achieve the desired appearance and functionality. Quality control measures, including dimensional checks and inspection, are performed to ensure the part meets specifications.
Benefits of CNC Milling:
- Precision and Accuracy: CNC milling enables the production of highly accurate components with tight tolerances, ensuring consistent quality and fit.
- Efficiency and Productivity: The automated nature of CNC milling reduces human error, speeds up production, and enables 24/7 operation, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity.
- Versatility: CNC milling machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. They can create complex shapes, and intricate details, and even produce multi-axis machined parts.
- Reproducibility: CNC milling ensures the repeatability of production processes, allowing for the creation of identical parts with minimal deviation.
Applications of CNC Milling:
CNC milling finds applications across various industries, including:
- Aerospace: Producing aircraft components with high precision and structural integrity.
- Automotive: Creating engine parts, molds, and prototypes.
- Medical: Manufacturing surgical instruments, prosthetics, and orthopedic implants.
- Electronics: Crafting intricate circuit boards and housings.
- Prototyping: Rapidly iterating designs and producing functional prototypes.
CNC milling is an invaluable manufacturing process that empowers industries to create intricate and precise components with remarkable efficiency. Its combination of computerized control, precision cutting tools, and versatile machining capabilities has transformed the way we design, prototype, and produce a wide range of products. As technology continues to advance, CNC milling will undoubtedly play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing and engineering.
